The family pedigree below demonstrates X-linked recessive transmission. Which of the following females is LEAST likely to be a heterozygote for the X-linked recessive allele? And give a brief reason for your answer. (Compare your answer to that provided at the end of the notes.)
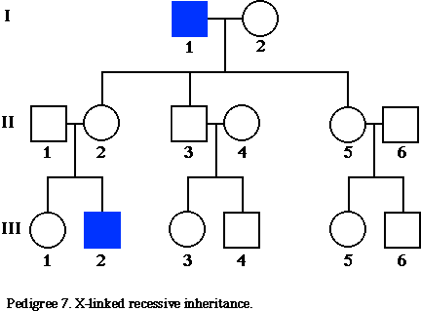
III-1
Incorrect
III-3
Correct! III-3. III-1 and III-5 each have a 50% chance of being a carrier but III-3 has almost a 0 chance of being a carrier. II-2 and II-5 are both obligate carrier because their father was affected and passed on his only X chromosome to his daughters. II-3 cannot be a carrier because males are never carriers (only affected or normal) and he did not inherit his father’s X chromosome. Instead, he inherited his father’s Y chromosome. III-3 couldn’t have been a carrier because neither her father nor her mother had the mutant gene (unless II-4 who married II-3) was a carrier transmitted through her own family- very unlikely).
III-5
Incorrect
Once a cell undergoes X-inactivation, all of its daughter cells will have the same X chromosome inactivated.
True
Correct!
False
Early in embryonic development in females, one of the two X chromosomes is randomly and permanently inactivated in cells other than egg cells.
What is the primary mechanism of genomic imprinting:
Nondisjunction events in meiosis
Incorrect
Different methylation patterns by gender
Correct! Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic alteration where genes are either silenced or expressed because of methylation patterns, depending on the parent the copy is inherited from.
Mosaicism occurring during mitosis
Incorrect
De novo during fertilization
Incorrect
Mitochondrial DNA differs from nuclear DNA in that it
crosses over within the same strand.
Incorrect
is inherited from the father only.
Incorrect
is present only in cells of the nervous and muscular systems.
Incorrect
is poorer at DNA repair
Correct! The mutation rate is faster in mtDNA partly because of few DNA repair mechanisms that are available to correct mistakes.